The Impact of School Size on Student Achievement
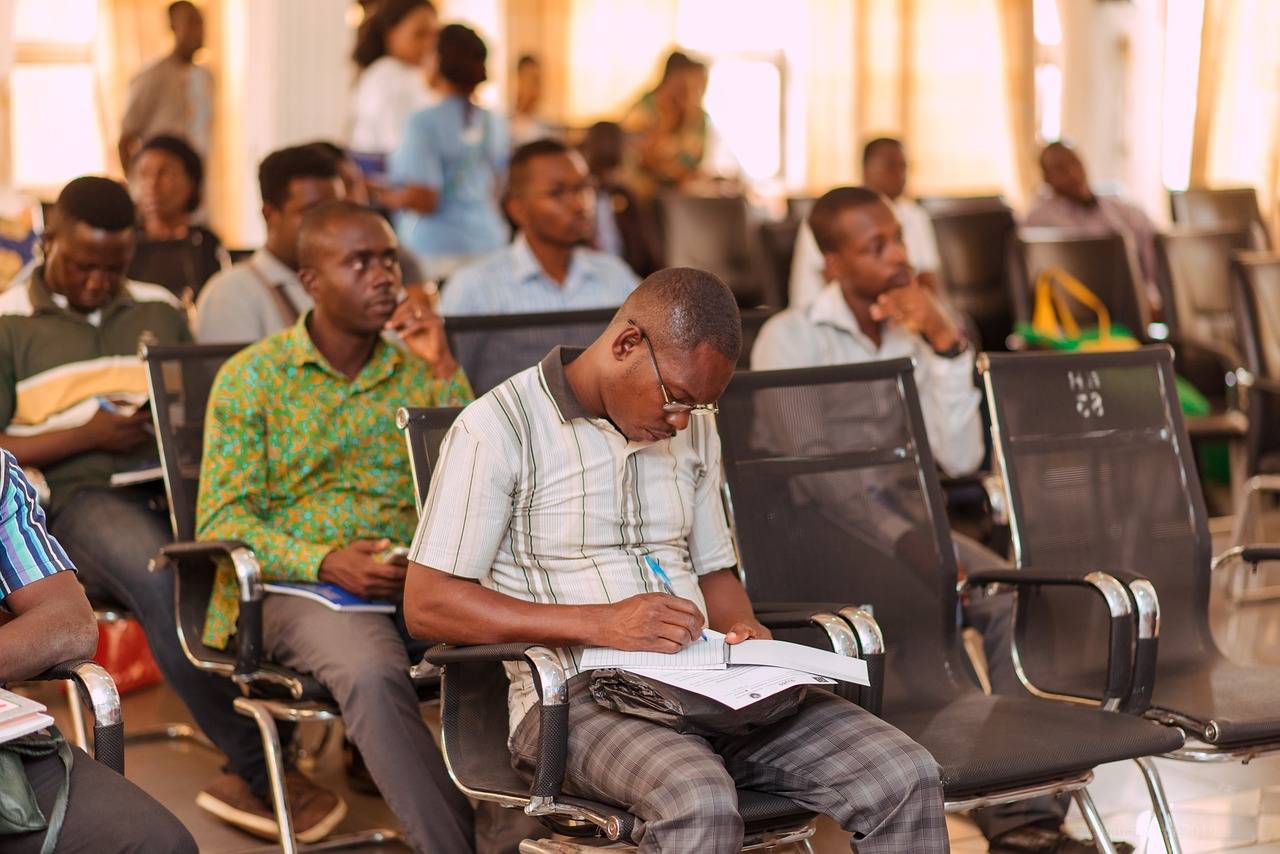
The size of a school is often influenced by various factors that play a significant role in shaping its structure and capacity. One of the key determinants is the geographical location of the school. Urban schools may tend to be larger in size due to higher population densities, while rural schools are typically smaller in scale as they serve fewer students within their vicinity. Additionally, the availability of resources and funding also impacts school size, with schools having more financial support being able to accommodate a larger student body.
Furthermore, the educational philosophy and curriculum offered by a school can influence its size. Schools that offer specialized programs or cater to specific educational needs may have a smaller student population compared to traditional comprehensive schools. In contrast, public schools that cater to a general student population may have a larger student body to accommodate diverse academic interests and abilities. Overall, the interplay of factors such as location, resources, and educational focus contribute to the determining school size in the educational landscape.
Relationship between school size and student-teacher ratio
School size has long been a topic of discussion in the educational system. Research suggests that smaller schools tend to have lower student-teacher ratios, leading to more individualized attention for students. Conversely, larger schools often face challenges in maintaining low student-teacher ratios due to the sheer volume of students enrolled.
The correlation between school size and student-teacher ratio underscores the importance of considering school size in educational policy and planning. Smaller schools inherently offer a more intimate learning environment where teachers can connect with students on a deeper level. On the other hand, larger schools must strategize ways to ensure that despite their size, students continue to receive adequate support and attention from their teachers.
How does school size affect the student-teacher ratio?
Generally, smaller schools tend to have lower student-teacher ratios as compared to larger schools. This is because smaller schools have fewer students per classroom, allowing teachers to give more individualized attention to each student.
What factors influence school size?
School size can be influenced by various factors such as population density in the area, economic conditions, government policies, and availability of resources. Additionally, the type of school (public, private, charter) and the grade levels offered can also impact school size.
Why is the student-teacher ratio important?
The student-teacher ratio is important because it can affect the quality of education and the overall learning experience for students. A lower student-teacher ratio typically allows for more personalized instruction, better classroom management, and increased student engagement.
How does the student-teacher ratio impact student achievement?
Research has shown that a lower student-teacher ratio is associated with improved student achievement. With fewer students to manage, teachers can provide more individualized support, feedback, and attention to each student, leading to better academic outcomes.
Are there any disadvantages to having a small student-teacher ratio?
While a small student-teacher ratio is generally beneficial, it can also pose challenges such as limited diversity of perspectives, fewer extracurricular opportunities, and higher costs for maintaining smaller class sizes. Schools must strike a balance between the benefits and drawbacks of a small student-teacher ratio.